Managing facilities involves a lot of moving parts, literally and figuratively. Trying to keep it all organized manually can be almost impossible, especially with goals to optimize costs, streamline processes and more. A CMMS can help maintenance professionals identify, track, locate and analyze all corporate assets, labor and material costs.
Some of the most beneficial aspects of a CMMS are the reporting and dashboard capabilities. These features help organizations take data on daily activities and turn them into meaningful insights to drive data-driven decision making. There are 95 pre-loaded reports on eMaint CMMS, but there are hundreds more reports to help organizations boost operational efficiency. We put together a list of five reports to get you started. Check them out below:
Preventive Maintenance (PM) Summary
PM summary reports enable organizations see all PM tasks created, scheduled, sent, received and closed. Filters allow these fields to be sorted by department and date range. CMMS also provides the ability to view who assigned specific requests, the location of the labor and associated activities.
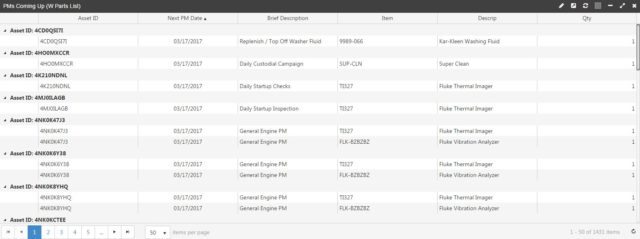
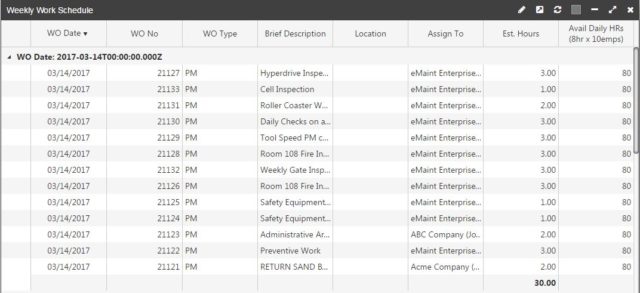
Work Orders
For a view of scheduled, open, and closed work orders, a work order summary report is helpful to leverage within a CMMS. Reports can be filtered by work order completion rate, past due work orders and requests, unscheduled work, and more.
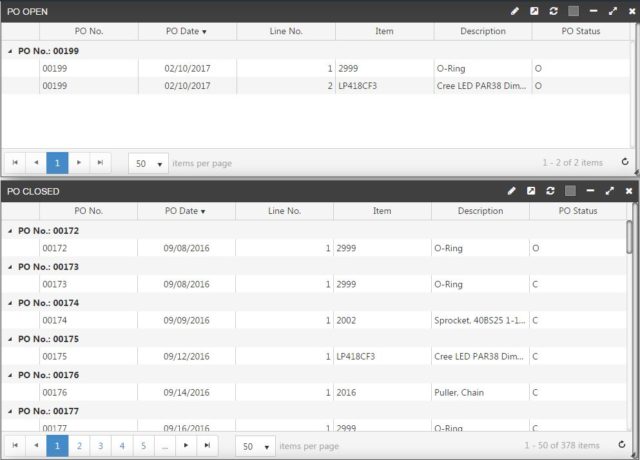
Purchase Orders
Purchasing summary reports help organizations keep track of all purchase orders. These reports include details throughout the purchasing journey. They can also be categorized by priority, purchase type, date, status, etc.
Equipment History
Equipment history reports empower organizations to track and analyze equipment by work order, purchasing, PM schedules, etc. This data can help provide insight into the health of assets, and inform repair vs. replace decisions.
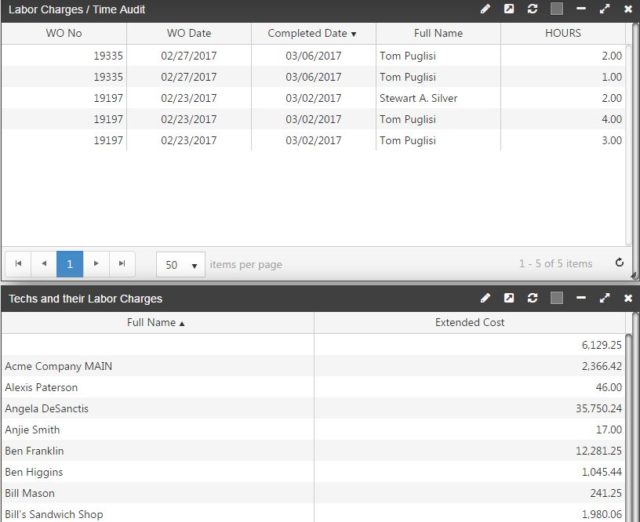
Labor Summary
Keep tabs on all associated labor based on work orders, purchase orders and preventive maintenance. These summaries can be sorted by priority, labor changes, date assigned or created, as well as who made the request and who the work was assigned to.